Confirmation Of Tonsillectomy Effectiveness In Treating IgAN
New papers in the medical literature provide powerful support for tonsillectomy at a primary treatment option for IgA Nephropathy
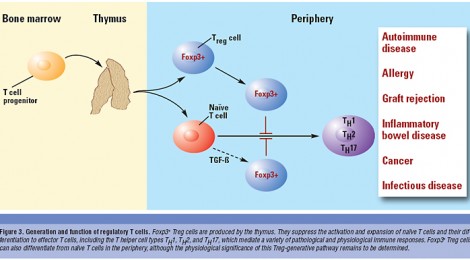
T Cells and related CD cells Produced By Tonsils (a thymus related gland), the primary source of kidney damage, are shown to be effectively reduced by tonsillectomy
A new paper is out where the researchers have studied the circulating T cells, T for thymus derived cells, in before and after tonsillectomy studies of patients with biopsy proven IgAN. The results show that the T cells decreased along with correlated negative effects known to be key issues in IgA Nephropathy. This very specific and clear finding unequivocally confirms the utility of tonsillectomy in treating IgAN.
Given these findings of a certain cause and effect action the present medical practice of NOT using tonsillectomy as a treatment for IgA Nephropathy and the equally ill conceived practice where tonsillectomy is prescribed only in late stages of IgAN are shown to be medical folly.
If you are in discussion with your nephrologist about tonsillectomy you might refer them to this important new work as these papers will inspire their confidence!
New paper on effective reduction of root cause of IgAN
Int Urol Nephrol. 2014 Oct 4. [Epub ahead of print]
CD4 +CD 25 +Treg cells and IgA nephropathy patients with tonsillectomy: a clinical and pathological study.
Huang H1, Sun W, Liang Y, Peng Y, Long XD, Liu Z, Wen X, Jia M, Tian R, Bai C, Li C.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
The relationship between tonsillar autoimmune response and the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy (IgAN) has been previously demonstrated. However, the role of CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells, which play critical roles in maintaining peripheral tolerance and preventing autoimmunity, has not yet been defined in IgAN.
METHODS:
Thirty-five patients with IgAN and 35 patients without renal disease were studied. The CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells were examined by flow cytometry. Clinical and laboratory data, such as serum creatinine and urinary samples, were obtained from each patient. Glomerular injury was assessed by histopathology. Serum IgA, C3, IL-2, IL-4 and IL-6 were analyzed by ELISA.
RESULTS:
CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells significantly decreased in IgAN patients compared with the controls before tonsillectomy (p < 0.05). CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells were negatively correlated with blood urea nitrogen, supernatant IL-4 and proteinuria in IgAN patients, and positively with estimated glomerular filtration rate. CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells gradually decreased as the severity of renal histology increased. In addition, serum IgA, IL-2, IL-6 and supernatant IL-4 elevated while CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells decreased in IgAN patients. CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells were significantly increased when serum IgA, IL-2, IL-6 and supernatant IL-4, urine protein and urine erythrocytes were decreased after tonsillectomy in patients with IgAN, but were still lower than those of the controls (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells were associated with IgAN, and tonsillectomy may increase CD4 +CD25 +Treg cells in IgAN patients, leading to clinical improvement.
———————————————-
Supporting the paper above are these independent papers showing the pivotal role of CD4 and T cells and tonsillectomy in the progression of IgAN
Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Sep 30. doi: 10.1111/cei.12461. [Epub ahead of print]
Combined C4d and CD3 immunostaining predicts IgA nephropathy progression.
Faria B1, Henriques C, Matos AC, Daha MR, Pestana M, Seelen M.
Abstract
A number of molecules have recently been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis and progression of IgA nephropathy (IgAN). Among these, we have selected C4d (complement lectin pathway involvement), CD3 (T-cell marker, traducing interstitial inflammation), Transglutaminase 2 (TGase-2, involved in tissue fibrosis development), and p-ERK 1/2 (protein kinase intracellular signaling molecule) to perform a panel of immunohistological biomarkers, and assess its predictive value for disease progression Immunohistochemical staining of these biomarkers was performed in paraffin sections from 74 renal biopsy cases with the clinical diagnosis of IgAN. Association between score analysis of these parameters and disease course was assessed through univariate and multivariate analysis, including baseline clinical and histological data. Univariate analysis showed that glomerular C4d, tubulointerstitial TGase2 and CD3 scores were associated with baseline proteinuria and disease progression. Multivariate analysis showed that only baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), C4d and CD3 were independently associated with progressive kidney disease (decline of at least 50% in the eGFR or progression to ESRD during the follow-up period). Establishing an accurate prediction model for IgAN progression is still a matter of research in clinical nephrology. The complement system, particularly lectin pathway activation, and T cell activation, have previously been shown to be potential modifiers of the disease course. Here we show that the combination of two histological biomarkers (C4d and CD3) can be a powerful predictor of IgAN progression and a potential useful tool for the clinical approach of this disease.
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Autoimmunity; Complement; T-cells
PMID: 25267249 [PubMed – as supplied by publisher]
———————————————-
Int Urol Nephrol. 2014 Nov;46(11):2175-82. doi: 10.1007/s11255-014-0818-7. Epub 2014 Sep 3.
Effect of tonsillectomy and its timing on renal outcomes in Caucasian IgA nephropathy patients.
Kovács T1, Vas T, Kövesdy CP, Degrell P, Nagy G, Rékási Z, Wittmann I, Nagy J.
Abstract
PURPOSE:
The role of tonsillectomy in the treatment of IgA nephropathy in Caucasian patients is controversial.
METHODS:
A retrospective cohort study was conducted in 264 patients with biopsy-proven primary IgA nephropathy to examine the association between tonsillectomy and long-term renal survival, defined as the incidence of estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFRs) of ≤30 ml/min/1.73 m(2) or end-stage renal disease (the composite of initiation of dialysis treatment or renal transplantation). The association of tonsillectomy with renal end-points was examined using the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox models.
RESULTS:
One-hundred and sixty-six patients did not undergo tonsillectomy (Group I, follow-up 130 ± 101 months) and 98 patients underwent tonsillectomy (Group II, follow-up 170 ± 124 months). The mean renal survival time was significantly longer for both end-points between those patients who underwent tonsillectomy (Group II) versus patients without tonsillectomy (Group I) (p < 0.001 and p = 0.005). The mean renal survival time was significantly longer for both end-points between those patients who had macrohaematuric episodes versus patients who had no macrohaematuric episodes (p = 0.035 and p = 0.019). Tonsillectomy, baseline eGFR and 24-h proteinuria were independent risk factors for both renal end-points.
CONCLUSION:
Tonsillectomy may delay the progression of IgA nephropathy mainly in IgA nephropathy patients with macrohaematuria. Prospective investigation of the protective role of tonsillectomy in Caucasian patients is needed.
PMID: 25181956 [PubMed – in process]
———————————————-
Int J Otolaryngol. 2014;2014:451612. doi: 10.1155/2014/451612. Epub 2014 May 19.
The Relationship between the Efficacy of Tonsillectomy and Renal Pathology in the Patients with IgA Nephropathy.
Nomura T, Makizumi Y, Yoshida T, Yamasoba T.
Abstract
Objective. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of tonsillectomy as a treatment for IgA nephropathy in relation to renal pathological findings. Methods. This is a retrospective analysis of 13 patients having IgA nephropathy treated by tonsillectomy. Results. UP/UCre levels decreased from 820.8 to 585.4 one month postsurgery and then showed slight worsening to 637.3 at the most recent follow-up. There was no significant difference in the improvement rate between pathological grades I-III and IV. There was positive correlation between Pre-UP/UCre level and the reduction rate of UP/UCre, which was statistically significant (R = 0.667, R (2) = 0.445, and P = 0.01). Conclusions. Reduction of UP/UCre at one month postsurgery is considered to be an overall prognostic factor, and tonsillectomy is considered to be an effective therapy for IgA patients regardless of the grade of renal pathology.
PMID: 24959178 [PubMed] PMCID: PMC4052205 Free PMC Article
———————————————-
What if you have IgAN and your tonsils are long gone?
This is not an unknown condition as our auto-immune systems are much larger than our tonsils alone. The thymus derived part of our immune system which is the root of all evil for those of us with IgA Nephropathy remains buried deep within our bodies. The tonsils just happen to be a major part of this Thymus derived system that are easy to excise.
The second line of action is the use of chemical immune system suppressing medications. First and oldest of these are steroids followed by the more modern alternative like mycophenolate mofetil. Any number of other modern immune system suppressors can be added to this list.
Recent Comments