IgAN Thymus Immune System Role Fortified By IgG Auto-Antibody Finding
IgG Auto-Immune Response In IgA Nephropathy
IgA nephropathy is second only to diabetic kidney disease in prevalence
Second Autoimmune Attack Vector, Missed In Routine and Biopsy Diagnosis, Is Now Confirmed
Again The Primitive Thymus Immune System Is Shown To Be The Source Of This Common Auto-Immune Disorder
IgA nephropathy is known to be caused in susceptible people by IgA immune complexes principally derived in the thymus and related immune system, especially the tonsils. These immune proteins, IgA and IgG are dangerously deposited in the kidneys delicate glomeruli — the filtering apparatus of the kidneys. When kidney glomeruli become damaged by the IgA deposits, crescents, the kidneys lose their ability to remove waste from the blood and to prevent leakage of vital blood proteins. This injury can lead to kidney failure.
This work is reported in the Journal of American Society For Nephrology August 2019.
With a second tonsillar auto-immune protein identified as causative in IgAN, the case for tonsillectomy as first-line treatment is made more important. Click to read more.
Up to now, IgA nephropathy kidney biopsies have exclusively focused on detecting IgA deposits in the kidneys. This main immunoglobulin is detected in the glomeruli by a clinical/biopsy test called routine immunofluorescence. But those singularly standard tests have failed to detect immunoglobulin IgG, which was believed to be another potential and potent contributor to the disease.
Now a study published in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology by researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham largely validates the hypothesis this second immunoglobulin, IgG, is a crucial part of the pathogenic immune deposits in patients with IgA nephropathy. Up to now, routine immunofluorescence microscopy — which identifies the presence of IgA in all cases of IgA nephropathy — failed to show IgG in 50 to 80 percent of kidney biopsies. In addition, IgG found in those positive tests had never been tested for antigenic specificities, such as specificity involving IgA.
UAB researchers hypothesized that the IgA was blocking the IgG from being detected in routine immunofluorescence microscopy, say co-corresponding authors Dana Rizk, M.D., and Jan Novak, Ph.D. They thought to use a different reagent, a small nanobody that detects the very end of the IgG molecule. When doing so IgG was detected in all biopsy specimens, including those that did not show IgG by routine immunofluorescence. Moreover, a highly sensitive confocal microscopy showed co-localization of the IgA1 and IgG in glomerular deposits of the biopsy-tissue specimens.
Furthermore, the IgG that UAB researchers extracted from both groups of biopsies specifically bound to the galactose-deficient IgA1, the glycoform of IgA1 that is known to be elevated in IgA nephropathy. The IgG auto-antibody specific for galactose-deficient IgA1 was not found in control extracts from two other forms of glomerulonephritis that do not involve galactose-deficient IgA1 — primary membranous nephropathy and lupus nephritis. These tests together confirmed that the IgG autoantibodies specific for galactose-deficient IgA1 are unique for immuno-deposits of patients with IgA nephropathy.
“These results reveal, for the first time, that IgA nephropathy kidney biopsies, with or without IgG by routine immunofluorescence, contain IgG autoantibodies specific for galactose-deficient IgA1,” Novak said. “These findings support the importance of these autoantibodies in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy.”
“These IgG autoantibodies specific for galactose-deficient IgA1are present also in blood of patients with IgA nephropathy, and the autoantibody levels predict disease progression. Thus, we can measure these autoantibodies in blood to identify patients who could benefit from a future disease-specific therapy, or monitor patients for responses to the therapy,” Novak said. “And better understanding of these autoantibodies can help us to develop new, disease-specific treatments for IgA nephropathy.”
The study, Novak and Rizk say, largely validates the four-hit hypothesis of IgA nephropathy pathogenesis:
1) Patients with IgA nephropathy have elevated levels of circulatory galactose-deficient IgA1;
2) This leads to the development of autoantibodies, mostly of the IgG subclass;
3) The IgG autoantibodies bind galactose-deficient IgA1 to form pathogenic immune complexes; and
4) Those pathogenic immune complexes deposit in glomeruli to incite kidney injury.
Further support for this hypothesis comes from multiple findings. For example, previous studies showed that IgA1 immuno-deposits in IgA nephropathy are enriched for galactose-deficient IgA1, likely originating from the IgA1-IgG complexes formed in the circulation. This study thus provided a key piece of evidence for the pathogenic role of IgG autoantibodies in IgA nephropathy.

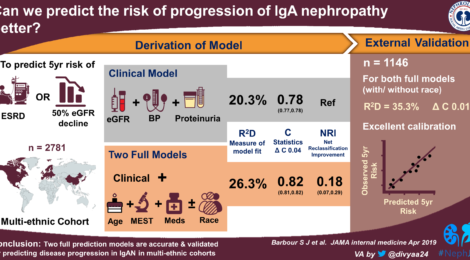
Prof. Novak of Birmingham
At UAB, Novak is professor in the UAB Department of Microbiology and Rizk is associate professor in the UAB Department of Medicine’s Division of Nephrology. She also directs clinical trials research in that division.
Co-authors with Rizk and Novak in the JASN paper, “Glomerular immuno-deposits of patients with IgA nephropathy are enriched for IgG autoantibodies specific for galactose-deficient IgA1,” are Manish K. Saha and Bruce A. Julian, Division of Nephrology, UAB Department of Medicine; Stacy Hall, Rhubell Brown and Zhi-Qiang Huang, UAB Department of Microbiology; and Huma Fatima and Lea Novak, UAB Department of Pathology.
Jan Novak and Bruce Julian designed the study. Support came from National Institutes of Health grants DK078244 and DK082753, and from a gift from the IGA Nephropathy Foundation of America. Manish Saha had support from NIH T32 training grant DK07545.
Recent Comments